Deploy a Solidity Contract using Cadence
Why Solidity And Cadence?
Solidity powers Ethereum's vast ecosystem, with a deep library of contracts like ERC721s for NFTs and a huge developer base. Deploying Solidity contracts on Flow's EVM layer leverages Flow's consensus for lower fees, quicker transactions, and slick asset handling, while giving you access to additional tools, including native VRF.
Imagine gaming NFTs minted cheaper, DeFi logic ported without rewrites, or Ethereum projects tapping Flow's scalable, user-first design. Flow EVM runs Solidity natively, and Cadence bridges the gap—letting you reuse trusted contracts while unlocking Flow's edge.
Objectives
After completing this guide, you'll be able to:
- Deploy a Solidity contract on Flow EVM using Cadence
- Call functions on this contract from the Cadence side
Prerequisites:
- NodeJs and NPM (must be installed - follow this guide)
- Go
- Flow Command Line Interface (Flow CLI) (must be installed - follow this guide)
- Remix (can be accessed online - available at Remix)
- Overflow (must be installed - install via Go with
go get github.com/bjartek/overflow/v2) - Cadence Owned Account (COA) (must be created - follow this guide to set up)
For this guide, we're using Remix for Solidity contract compilation and Overflow for running Cadence transactions on Flow EVM. To deploy a Solidity contract using Cadence, you'll need a Cadence Owned Account; the guide linked above explains how to create one.
High-Level Walkthrough
At a high level, this guide walks you through deploying a Solidity contract on the Flow blockchain's EVM layer using Cadence in three main steps:
-
Compile the Solidity Contract: You'll start by taking a Solidity contract (like an ERC721 for NFTs) and compiling it into bytecode using Remix, an online Ethereum development tool. This bytecode is the machine-readable version of your contract, ready to be deployed.
-
Deploy to Flow EVM with Cadence: Next, you'll set up a local environment with tools like Overflow and the Flow CLI. Using a Cadence transaction, you'll deploy the bytecode to Flow's EVM layer via a Cadence Owned Account (COA), bridging the two ecosystems seamlessly.
-
Interact from Cadence: Finally, you'll use a Cadence script to call a function on your deployed Solidity contract—like minting an NFT—demonstrating how Cadence can interact with Ethereum-style logic on Flow.
This process leverages Ethereum's robust contract library and Flow's efficient, user-friendly blockchain, opening up a world of cross-platform possibilities—all in a few straightforward steps.
Step 1: Compile the Solidity Contract
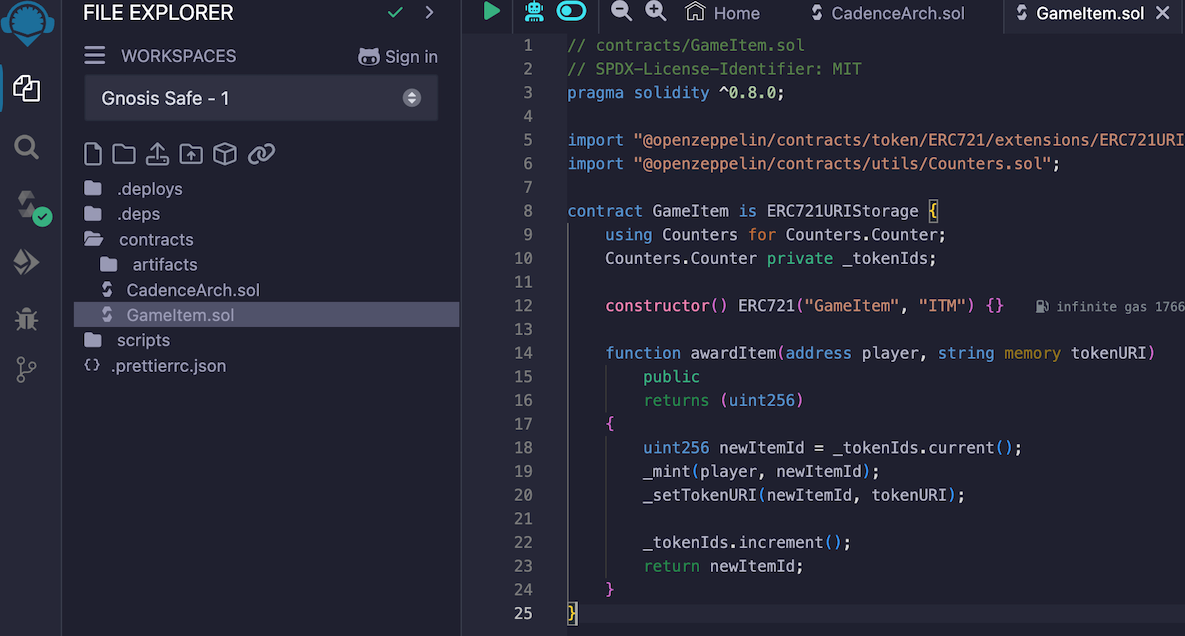
Start by compiling your Solidity contract to get its bytecode. For this example, use OpenZeppelin's ERC721 contract for tracking game items. Here's how to do it in Remix:
- Open Remix: Go to Remix in your browser.
- Create a New File: In the Remix file explorer, click the "+" button and name the file (e.g.,
GameItem.sol). - Paste the Contract Code: Copy the OpenZeppelin ERC721 contract code (e.g., from this example) and paste it into the new file.
- Compile the Contract:
- Select the appropriate Solidity compiler version (e.g., 0.8.x) in the "Solidity Compiler" tab.
- Click "Compile GameItem.sol".
- Copy the Bytecode:
- Go to the "Compilation Details" (or "Bytecode" section after compilation).
- Copy the "object" field under the bytecode section.
- Save the Bytecode:
- From your project's root directory, create a folder named
bytecode. - Inside it, create a file called
GameItem.js. - Paste the bytecode into
GameItem.jsas a string (e.g.,module.exports = "0x...").
- From your project's root directory, create a folder named
Here's the Cadence transaction we'll use later to deploy this bytecode on Flow EVM:
_15import "EVM"_15_15transaction(code: String, pathId: Int) {_15 let coa: auth(EVM.Deploy) &EVM.CadenceOwnedAccount_15_15 prepare(signer: auth(Storage) &Account) {_15 let coaPath = StoragePath(identifier: signer.address.toString().concat("EVM_").concat(pathId.toString()))!_15 self.coa = signer.storage.borrow<auth(EVM.Deploy) &EVM.CadenceOwnedAccount>(_15 from: coaPath) ?? panic("Could not borrow reference to the COA!")_15 }_15_15 execute {_15 self.coa.deploy(code: code.decodeHex(), gasLimit: 15000000, value: EVM.Balance(attoflow: 0))_15 }_15}
Step 2: Set Up Your Environment and Deploy the Contract
To run the transactions and tests, we'll use Overflow. Follow these steps to set up and deploy:
- Initialize a Go Project:
- Open your terminal and navigate to your project's root directory.
- Run:
go mod init flow/tutorialsto create a Go module.
- Install Overflow:
- Run:
go get github.com/bjartek/overflow/v2to install the Overflow package.
- Run:
- Create the Task File:
- In the root directory, create a folder called
tasks. - Inside
tasks, create a file namedmain.go. - Paste the following Go code into
main.go:
- In the root directory, create a folder called
_41package main_41_41import (_41 "fmt"_41 "io/ioutil"_41 "log"_41 . "github.com/bjartek/overflow/v2"_41 "github.com/fatih/color"_41)_41_41func readJSFile(filePath string) (string, error) {_41 content, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filePath)_41 if err != nil {_41 return "", err_41 }_41 return string(content), nil_41}_41_41func main() {_41 filePath := "bytecode/GameItem.js"_41 jsContent, err := readJSFile(filePath)_41 if err != nil {_41 log.Fatalf("Error reading JavaScript file: %v", err)_41 }_41 o := Overflow(_41 WithGlobalPrintOptions(),_41 WithNetwork("testnet"),_41 )_41_41 color.Red("Should be able to create a COA")_41 o.Tx("create_COA",_41 WithSigner("gamer"),_41 ).Print()_41_41 color.Cyan("Deploy a Solidity contract to Random's COA")_41 o.Tx("deploy_sol_contract",_41 WithSigner("gamer"),_41 WithArg("code", jsContent),_41 WithArg("pathId", 0),_41 ).Print()_41}
- Run the Deployment:
- From the terminal, navigate to the root directory.
- Run:
go run ./tasks/main.go. - This will:
- Create a Cadence Owned Account (COA) for the "gamer" account.
- Deploy the Solidity contract using the bytecode from
GameItem.js.
- Verify the Deployment:
- Check the terminal output for the deployed contract address (e.g.,
0xb93cB988D0722E17B67A5E169a47FB6F3A4dea1b). - Visit the Flow EVM Testnet Scanner and search for the address to confirm the deployment.
- Check the terminal output for the deployed contract address (e.g.,
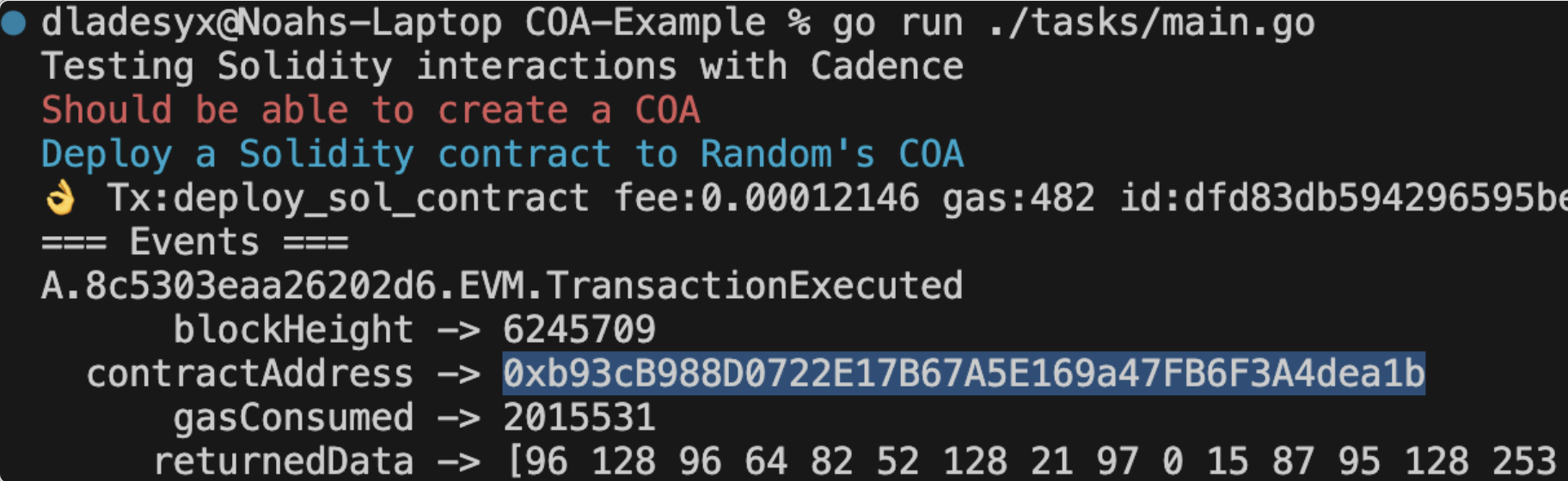
Note: The "gamer" account (e.g., 0xb995271139c0126f) is a Testnet account. The pathId (set to 0) corresponds to the COA slot. If you've created multiple COAs, increment pathId (e.g., 1, 2) accordingly.
Step 3: Call a Function on the Deployed Contract
Now, let's call the awardItem function from the deployed ERC721 contract using this Cadence script:
- Cadence Script Preparation: Use the following Cadence script to call the contract function:
_23import "EVM"_23_23access(all)_23fun main(hexEncodedAddress: String, address: Address, pathId: UInt64): [AnyStruct] {_23 let account = getAuthAccount<auth(Storage) &Account>(address)_23 let coaPath = StoragePath(identifier: address.toString().concat("EVM_").concat(pathId.toString()))!_23 let coa = account.storage.borrow<auth(EVM.Call) &EVM.CadenceOwnedAccount>(_23 from: coaPath_23 ) ?? panic("Could not borrow reference to the COA!")_23 let addressBytes = hexEncodedAddress.decodeHex().toConstantSized<[UInt8; 20]>()!_23_23 let callResult = coa.call(_23 to: EVM.EVMAddress(bytes: addressBytes),_23 data: EVM.encodeABIWithSignature(_23 "awardItem(address,string)",_23 [EVM.addressFromString("000000000000000000000002A16A68E971e4670B"), "{name: gamerz}"]_23 ),_23 gasLimit: 15000000,_23 value: EVM.Balance(attoflow: 0)_23 )_23_23 return EVM.decodeABI(types: [Type<UInt256>()], data: callResult.data)_23}
- Update the Go File:
Open
tasks/main.goand add the following code at the end of themainfunction (replace thehexEncodedAddresswith your deployed contract address):
_10color.Cyan("Mint a game item from the Solidity contract")_10o.Script("call_sol_function",_10 WithArg("hexEncodedAddress", "b93cB988D0722E17B67A5E169a47FB6F3A4dea1b"),_10 WithArg("address", "gamer"),_10 WithArg("pathId", 0),_10).Print()
-
Run the Script:
- In the terminal, run:
go run ./tasks/main.goagain. - This executes the Cadence script, calling
awardItemto mint an NFT.
- In the terminal, run:
-
Check the Result:
- The terminal will display the token ID of the newly minted NFT (e.g., a UInt256 value).
- See the screenshot below for an example output:
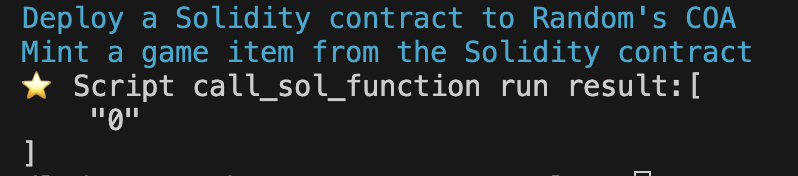
The terminal output shows the unique token ID that was generated when minting the game item through the Solidity contract using Cadence.
The awardItem function is called with a test address and a string parameter. In a real-world scenario, you would replace these with actual wallet addresses and more meaningful metadata.
Conclusion
Deploying a Solidity contract within a Cadence environment on the Flow blockchain is not only feasible but also presents an exciting opportunity for you to harness the strengths of both programming languages. Throughout this guide, you've navigated the critical steps involved in the deployment process, from compiling your Solidity contract using Remix to executing transactions with Overflow and Cadence scripts. By completing this guide, you've achieved the following:
- Deployed a Solidity contract on Flow EVM using Cadence: You compiled and deployed your Solidity contract to Flow's EVM layer via a Cadence transaction.
- Called functions from Cadence: You used a Cadence script to mint an NFT by invoking the
awardItemfunction on your deployed contract.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, adopting these best practices is crucial for fostering a secure and trustworthy ecosystem. This empowers you to innovate while staying true to the core principles of decentralization and fairness.